Long time ago, I lower the MTU of my router to solve a networking issue (see my previous blog entry). However, it is not the end of story.
Recently, I have changed my job. My new company provides Citrix Presentation Server for employees to work at home via remote desktop.
Then, at home, I tried to connect to Citrix server and run remote desktop. I can login but the link is very unstable. It disconnected every 10 to 20 seconds.
After some investigation, I found it is the MTU problem again. The problem is fully explained at the following site:
http://www.netheaven.com/pmtu.html
I should change the MTU of my desktop at home to match the router. Finally, it works!
Saturday, August 25, 2007
Sunday, July 01, 2007
Boost C++ Libraries
Recently, I checked some job ad. on the web and found some jobs require knowledge about "Boost". I have not heard "Boost" before. After some googling, I visit the web site of Boost. Boost is really a great thing. It is a set of C++ libraries contains many useful programming constructs with good documentation, e.g. smart pointers, regular expression, object pools, state machines.... Lastly, it is open source and free.
Sunday, June 17, 2007
Dig out dead looping thread
It is not easy to write multi-threading applications. One of the common bugs is dead looping of a thread. To kill this kind of bugs, the first step is to find out which thread causes dead looping. However, an application may have dozens of threads. How to dig out the dead looping thread? My trick is to issue the
ps -eLf command to list the information of threads in the whole system. The "time" column of the output of ps shows the CPU time have spent by the threads. Most likely, the dead looping thread would be the thread spending most CPU time. Then, drop down the LWP number of the thread. Next, you use gdb to attach the process and to debug the thread.
Sunday, June 10, 2007
Job Interview Questions
Recently, I got some job interviews. The interviewers asked me tones of questions. Most of them were very technical. The most difficult question was an IQ puzzle. Under stress, it is difficult to overclock my brain :<
At home, I found a web site which included the IQ puzzle:
http://www.techinterview.org/index.html
At home, I found a web site which included the IQ puzzle:
http://www.techinterview.org/index.html
Saturday, May 12, 2007
Undefined symbols in C++
In C++ programming, we sometimes encounter "undefined symbols" problem during compilation or dlopen. The name of undefined symbols looks obfuscated. E.g.:
To translate the mangled symbols to more meaningful text, we can use the
Unable to dlopen(test.so): test.so: Undefined symbol "_ZN6moduleD2Ev"You may wonder why the symbol looks so ugly. Actually, this conversion of symbol is called name mangling. C++ supports polymorphism, this means functions can have same name but different types and numbers of parameters. Therefore, compiler cannot just use the function name as the symbol. Instead, both function name and parameter types should be included in symbol naming. Name mangling is the technique to encode a function name and parameter types into one symbol.
To translate the mangled symbols to more meaningful text, we can use the
c++flit utility. E.g.ahlam@oxygen:~$ c++filt _ZN6moduleD2EvNow, you know "_ZN6moduleD2Ev" is the destructor of
module::~module()
class module.
Friday, May 11, 2007
More than "command not found"
In old days, if I try to run a command which doesn't exist in my Linux box, it just prompts "command not found". Today, Ubuntu gives me a nice response:
It's surprising!
ahlam@oxygen:/usr/bin$ cdecl
The program 'cdecl' can be found in the following packages:
* cutils
* cdecl
Try: sudo apt-get install <selected package>
Make sure you have the 'universe' component enabled
bash: cdecl: command not found
It's surprising!
Wednesday, May 09, 2007
Using new Chinese fonts from M$
One of my friends told me that the Chinese fonts in M$ Vista is much more beautiful. So, I try to install the fonts to my Ubuntu box today. The new Chinese fonts called YaHei and JhengHei. If you don't have Vista, you can download from somewhere (:P). The screenshot below shows the result.

For details about how to install the new fonts, you can refer to http://imtx.cn/feed.php?go=entry_332

For details about how to install the new fonts, you can refer to http://imtx.cn/feed.php?go=entry_332
Sunday, April 22, 2007
Upgrade to Ubuntu 7.04
Yesterday, I follow the instruction here to upgrade my Ubuntu to 7.04. Unfortunately, the Update Manager crashes during package installation. To solve the problem, I use the following command:
Then, I reboot the Linux box. Some errors occurs. It fails to mount all partitions, excepts "/" partition. After some investigation, under the new kernel (2.6.20), IDE harddisks/CD-ROM are considered as SCSI. The following is the
Therefore, the entries in
dpkg --configure -a
Then, I reboot the Linux box. Some errors occurs. It fails to mount all partitions, excepts "/" partition. After some investigation, under the new kernel (2.6.20), IDE harddisks/CD-ROM are considered as SCSI. The following is the
dmesg output:ata1: PATA max UDMA/100 cmd 0x000101f0 ctl 0x000103f6 bmdma 0x0001f000 irq 14
ata2: PATA max UDMA/100 cmd 0x00010170 ctl 0x00010376 bmdma 0x0001f008 irq 15
scsi0 : ata_piix
ata1.00: ata_hpa_resize 1: sectors = 156301488, hpa_sectors = 156301488
ata1.00: ATA-6: WDC WD800BB-55HEA0, 13.03G13, max UDMA/100
ata1.00: 156301488 sectors, multi 16: LBA
ata1.00: ata_hpa_resize 1: sectors = 156301488, hpa_sectors = 156301488
ata1.00: configured for UDMA/100
scsi1 : ata_piix
ATA: abnormal status 0x7F on port 0x00010177
ata2.01: ATAPI, max UDMA/33
ata2.01: configured for UDMA/33
scsi 0:0:0:0: Direct-Access ATA WDC WD800BB-55HE 13.0 PQ: 0 ANSI: 5
scsi 1:0:1:0: CD-ROM RW-481248 1.00 PQ: 0 ANSI: 5
Therefore, the entries in
/etc/fstab should be changed from "/dev/hdan" to "/dev/sdan".
Thursday, April 19, 2007
Know more about a process
Today, I would like to introduce some ways to get more information of a process, and hope those can help in trouble-shooting and debugging.
To list the environment variables of a process you can issue the command:
E.g.:
E.g:
To list the memory map of a process, you can use the
E.g:
In
For details, please
List environment variables
To list the environment variables of a process you can issue the command:
ps ewww pidE.g.:
ahlam@oxygen:~/test/malloc$ ps ewww 4752
PID TTY STAT TIME COMMAND
4752 pts/2 Ss+ 0:00 bash USER=ahlam HOME=/home/ahlam DESKTOP_SESSION=default GDM_XSERVER_LOCATION=loca
l GTK_IM_MODULE=gcin LOGNAME=ahlam USERNAME=ahlam GDM_LANG=en_HK.UTF-8 PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/u
sr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin/X11:/usr/games DISPLAY=:0.0 LANG=en_HK.UTF-8 XMODIFIERS=@im=gcin XAUTHOR
ITY=/home/ahlam/.Xauthority SHELL=/bin/bash GDMSESSION=default QT_IM_MODULE=gcin PWD=/home/ahlam SSH_AUTH_SOC
K=/tmp/ssh-nRdglP4521/agent.4521 SSH_AGENT_PID=4563 DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS=unix:abstract=/tmp/dbus-ix9My5o6
DJ,guid=8abd2646dc897f03d1cfb07e3a3d4b00 GTK_RC_FILES=/etc/gtk/gtkrc:/home/ahlam/.gtkrc-1.2-gnome2 SESSION_MA
NAGER=local/oxygen:/tmp/.ICE-unix/4521 GNOME_KEYRING_SOCKET=/tmp/keyring-fXmYul/socket GNOME_DESKTOP_SESSION_
ID=Default TERM=xterm COLORTERM=gnome-terminal WINDOWID=31457489
List out the threads of a process
ps ms pidE.g:
ahlam@oxygen:~/test/malloc$ ps ms 4752
UID PID PENDING BLOCKED IGNORED CAUGHT STAT TTY TIME COMMAND
1000 4752 0000000000000000 - - - - pts/2 0:00 bash
1000 - 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 0000000000384004 000000004b813efb Ss+ - 0:00 -
Print the memory map
To list the memory map of a process, you can use the
pmap command. It lists out the mapped memory regions and the purpose of the memory regions. It also lists out the .so files loaded by the process.pmap pidE.g:
ahlam@oxygen:~/test/malloc$ pmap 4752
4752: bash
08048000 644K r-x-- /bin/bash
080e9000 20K rw--- /bin/bash
080ee000 1804K rw--- [ anon ]
b7c94000 36K r-x-- /lib/tls/i686/cmov/libnss_files-2.4.so
b7c9d000 8K rw--- /lib/tls/i686/cmov/libnss_files-2.4.so
b7c9f000 32K r-x-- /lib/tls/i686/cmov/libnss_nis-2.4.so
b7ca7000 8K rw--- /lib/tls/i686/cmov/libnss_nis-2.4.so
b7ca9000 72K r-x-- /lib/tls/i686/cmov/libnsl-2.4.so
b7cbb000 8K rw--- /lib/tls/i686/cmov/libnsl-2.4.so
b7cbd000 8K rw--- [ anon ]
b7cbf000 28K r-x-- /lib/tls/i686/cmov/libnss_compat-2.4.so
b7cc6000 8K rw--- /lib/tls/i686/cmov/libnss_compat-2.4.so
b7cd7000 204K r---- /usr/lib/locale/en_HK.utf8/LC_CTYPE
b7d0a000 4K r---- /usr/lib/locale/en_HK.utf8/LC_NUMERIC
b7d0b000 4K r---- /usr/lib/locale/en_HK.utf8/LC_TIME
b7d0c000 860K r---- /usr/lib/locale/en_HK.utf8/LC_COLLATE
b7de3000 8K rw--- [ anon ]
b7de5000 1204K r-x-- /lib/tls/i686/cmov/libc-2.4.so
b7f12000 8K r---- /lib/tls/i686/cmov/libc-2.4.so
b7f14000 8K rw--- /lib/tls/i686/cmov/libc-2.4.so
b7f16000 12K rw--- [ anon ]
b7f19000 8K r-x-- /lib/tls/i686/cmov/libdl-2.4.so
b7f1b000 8K rw--- /lib/tls/i686/cmov/libdl-2.4.so
b7f1d000 220K r-x-- /lib/libncurses.so.5.5
b7f54000 32K rw--- /lib/libncurses.so.5.5
b7f5c000 4K rw--- [ anon ]
b7f5d000 4K r---- /usr/lib/locale/en_HK.utf8/LC_MONETARY
b7f5e000 4K r---- /usr/lib/locale/en_HK.utf8/LC_MESSAGES/SYS_LC_MESSAGES
b7f5f000 4K r---- /usr/lib/locale/en_HK.utf8/LC_PAPER
b7f60000 4K r---- /usr/lib/locale/en_HK.utf8/LC_NAME
b7f61000 4K r---- /usr/lib/locale/en_HK.utf8/LC_ADDRESS
b7f62000 4K r---- /usr/lib/locale/en_HK.utf8/LC_TELEPHONE
b7f63000 4K r---- /usr/lib/locale/en_HK.utf8/LC_MEASUREMENT
b7f64000 28K r--s- /usr/lib/gconv/gconv-modules.cache
b7f6b000 4K r---- /usr/lib/locale/en_HK.utf8/LC_IDENTIFICATION
b7f6c000 8K rw--- [ anon ]
b7f6e000 100K r-x-- /lib/ld-2.4.so
b7f87000 8K rw--- /lib/ld-2.4.so
bfa1c000 88K rw--- [ stack ]
ffffe000 4K ----- [ anon ]
total 5528K
/proc/pid
In
proc/pid directory, it contains much information of a process.
ahlam@oxygen:~/test/malloc$ ls -l /proc/4752
total 0
dr-xr-xr-x 2 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 20:17 attr
-r-------- 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 20:17 auxv
-r--r--r-- 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 19:57 cmdline
-r--r--r-- 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 20:17 cpuset
lrwxrwxrwx 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 18:20 cwd -> /home/ahlam/test/malloc
-r-------- 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 19:58 environ
lrwxrwxrwx 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 20:17 exe -> /bin/bash
dr-x------ 2 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 19:57 fd
-r--r--r-- 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 20:06 maps
-rw------- 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 20:17 mem
-r--r--r-- 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 20:17 mounts
-r-------- 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 20:17 mountstats
-rw-r--r-- 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 20:17 oom_adj
-r--r--r-- 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 20:17 oom_score
lrwxrwxrwx 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 20:17 root -> /
-rw------- 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 20:17 seccomp
-r--r--r-- 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 20:17 smaps
-r--r--r-- 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 19:57 stat
-r--r--r-- 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 20:17 statm
-r--r--r-- 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 19:57 status
dr-xr-xr-x 3 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 20:17 task
-r--r--r-- 1 ahlam ahlam 0 2007-04-19 20:17 wchan
For details, please
man proc.
Sunday, April 15, 2007
Optimistic memory allocation strategy in Linux
If you know C programming language, you must know what is
Reference:
man malloc
http://linux-mm.org/OOM_Killer
malloc. malloc is for dynamic memory allocation. In colleges, we learned that malloc should return NULL in case of out-of-memory. However, it is not the case in Linux. By default, Linux uses optimistic memory allocation strategy. Under this strategy, Linux assumes there always exists free memory. The memory region returns by malloc is not actually allocated until the process touches the memory region. This means the memory region returns by malloc may not be available. In case of out-of-memory, the OOM Killer in Linux will pick up one or more process to kill. This sounds strange!Reference:
man malloc
http://linux-mm.org/OOM_Killer
Friday, April 13, 2007
Change the title of xterm
In most modern Linux distribution, the title of terminal follows the working directory. The mechanism behind this feature is not simple. You can even customize the title. Please note that, in this article, it is assumed to use xterm and bash.
In xterm, the following escape sequence can change the title of terminal windows:
However, if you issue the above command in your terminal, the title may not be changed. It is because the
In the above command,
To customize your terminal title, you should update the value of
Reference:
How to change the title of an xterm
man bash

In xterm, the following escape sequence can change the title of terminal windows:
ESC]0;title_stringBELESC and BEL is 033 and 007 (in octal ASCII) respectively. For example, we can use the following echo command to set the terminal title as "Hello World.":echo -ne "\033]0;Hello World.\007"However, if you issue the above command in your terminal, the title may not be changed. It is because the
PROMPT_COMMAND environment variable have already been defined for changing the terminal title. The value in PROMPT_COMMAND environment variable will be executed as command prior to issuing each prompt. In my terminal, the value of PROMPT_COMMAND is:echo -ne "\033]0;${USER}@${HOSTNAME}: ${PWD/$HOME/~}\007"In the above command,
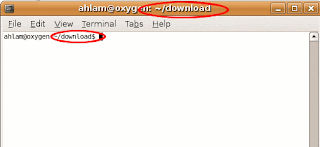
${USER} and ${HOSTNAME} is the username and hostname respectively, while the ${PWD/$HOME/~} is the current working directory with $HOME abbreviated as ~. Therefore, in my terminal, the title will be changed to show username, hostname and current working directory, e.g.:ahlam@oxygen: ~/downloadTo customize your terminal title, you should update the value of
PROMPT_COMMAND, e.g.:export PROMPT_COMMAND='echo -ne "\033]0;Hello World.\007"'Reference:
How to change the title of an xterm
man bash
Saturday, March 31, 2007
Adobe Reader crashes with SCIM
I am using Ubuntu 6.10. Recently, I have installed Adobe Reader 7.0.9. However, Adobe Reader crashed at startup. In ubuntuguide.org , it mentions Adobe Reader won't work with SCIM. Finally, I found the solution -- scim bridge. To solve the problem, install the scim-bridge package and edit the "acroread" script to insert the line "GTK_IM_MODULE=scim-bridge" at the beginning of the script, like:
Then, Adobe Reader launches normally!
#!/bin/sh
#
GTK_IM_MODULE=scim-bridge
...
Then, Adobe Reader launches normally!
Saturday, March 10, 2007
Be careful with STL strings
Please refer to the following C++ code fragment:
char charArray[4]={'a','b','c',0,};
string str1(charArray);
string str2;
str2.append(charArray, 4);Use the following lines to print out the contents of str1 and str2:cout << "str1 [" << str1 << ']' << endl;The output would be:
cout << "str2 [" << str2 << ']' << endl;
str1 [abc]Two strings looks same. However, does str1 equal to str2?
str2 [abc]
cout << (str1 == str2? "equal" : "not equal") << endl;The output:
not equalWhy not!? Let's print out the size of the strings:
cout << "str1 size = " << str1.size() << endl;The output:
cout << "str2 size = " << str2.size() << endl;
str1 size = 3In short, we should be careful about the == operator of strings. It does not only compare the contents of strings, but it also compares the size of strings.
str2 size = 4
Saturday, March 03, 2007
Does it really need to Lock?
In multi-threading environment, we always face the problem of race condition -- concurrent accessing sharing data among threads. To solve the problem, we can use locking primitives, e.g. mutex, to avoid concurrent accessing of sharing data. However, those locking primitives are expensive, since they involve system calls. In some cases, we can avoid using locks.
Counting
Suppose threads updating a count variable concurrently. To avoid race condition, I saw some implementation like:
Circular Buffers
In general, without locking, a circular buffer cannot be thread-safe. However, under a restricted condition and implementation, there would be no race condition problem. In short, for a fixed size circular buffer, if there is exactly one reader and one writer, it does not need locking. It is because the reader only updates the read-pointer and the writer only updates the write-pointer. This issue have been discussed in http://ddj.com/dept/cpp/184401814.
Counting
Suppose threads updating a count variable concurrently. To avoid race condition, I saw some implementation like:
mutex.lock();Increment an integer just takes one CPU instruction, but locking and unlocking of mutex takes hundreds or thousands of CPU instructions. To avoid race condition, we can use atomic operations provided by CPU. Referring to /usr/include/asm-i386, there is implementation of atomic add:
count++;
mutex.unlock();
static __inline__ void atomic_add(int i, atomic_t *v)In Apache Portable Runtime project, it provides a set of atomic operations for different platforms.
{
__asm__ __volatile__(
LOCK_PREFIX "addl %1,%0"
:"=m" (v->counter)
:"ir" (i), "m" (v->counter));
}
Circular Buffers
In general, without locking, a circular buffer cannot be thread-safe. However, under a restricted condition and implementation, there would be no race condition problem. In short, for a fixed size circular buffer, if there is exactly one reader and one writer, it does not need locking. It is because the reader only updates the read-pointer and the writer only updates the write-pointer. This issue have been discussed in http://ddj.com/dept/cpp/184401814.
Sunday, February 04, 2007
Is Port 25 blocked?
Port 25, default port of SMTP, is for E-mail transferring. To reduce SPAM, ISPs normally block this port, especially for those household DSL accounts. Therefore, people may think that it is impossible to setup E-mail server at home.
I have experiences of using HKBN and Netvigator, they are not really block all port 25 traffics. They only block outgoing traffics, but not incoming traffic. To setup the E-mail server, we can use the "smarthost" trick.
I have experiences of using HKBN and Netvigator, they are not really block all port 25 traffics. They only block outgoing traffics, but not incoming traffic. To setup the E-mail server, we can use the "smarthost" trick.
Saturday, January 27, 2007
Stack Size of Threads
Several months ago, my boss assigned me to do performance tuning on several applications. One of them was a server application, which was for distributing data to clients. This application used a lot of threads, two threads per client -.-" It can support up to about 80 clients. If the number was over 80, the application generated a core dump. The core dump was due to out of memory. From top, I found the virtual memory size increases 4x MB for each newly connected client. It confused me. How could one client eat 4xMB?
Finally, I found the answer -- stack size of a thread. In the Linux system, the default stack size of a thread (in case of pthread library) is set to 20MB!
To change the stack size of a thread,
Finally, I found the answer -- stack size of a thread. In the Linux system, the default stack size of a thread (in case of pthread library) is set to 20MB!
To change the stack size of a thread,
- use pthread_attr_setstacksize (&attr, stacksize) to set the attribute during thread creation. For more details, you can refer to the following link: http://www.llnl.gov/computing/tutorials/pthreads/#Stack
- use ulimit -s nnnn command to change the default stack size of pthread, where nnnn is the size in KBytes. (http://kbase.redhat.com/faq/FAQ_43_8710.shtm)
Saturday, January 20, 2007
Find files by last modification time
"find" is a powerful Unix/Linux utility for searching files. With the -mtime (or -mmin) options, "find" can search files which modified within a specific days (or minutes). However, there is no option for "find" to search files modified after a point of time. To do this, you need to write a shell script:
#!/bin/shThis script creates a temp file with a specific last modification time in /tmp directory and uses the temp file's last modification time as a reference time point for "find" to search files newer than the specific time. The -newer option of "find" is for searching files which are newer than a specific file. touch -t "$1" /tmp/$$ creates a temp file with a specific last modified time using the -t option.
touch -t "$1" /tmp/$$ \
&& find . -newer /tmp/$$ \
&& rm /tmp/$$
Sunday, January 14, 2007
Speed up DNS Lookup in Linux
When I was first time to use Linux for web surfing, I found it was slower than MS Windows. Recently, I found the reason form the Internet. The difference is due to the DNS lookup speed. In Windows, it caches DNS lookup results but Linux doesn't. To improve the lookup speed in Linux, we can install dnsmasq, which is a light-weight DNS server for Linux.
Monday, January 01, 2007
Bufferring Behaviour of stdout(Stardard Out)
Recently, I encounter a problem of capturing stdout of a program. The program is expected to run for a long time. When the output of the program is on the console, everything works fine. However, when the output of the program is redirected to a pipe or a file, the output is buffered for a long time. This means the output of the program is not appeared immediately. This behaviour is not desired. To illustrate the problem, I write the following simple program:
redirected to a pipe, like:
a.out | tee tmp.log
After some investigation, I found the behaviour is documented in setbuf(3) man page:
There are two ways to solve the problem. First, call fflush(stdout) after printf.
Second, call setlinebuf(stdout) at the startup of the program.
The program prints "hello!" for every second. However, the output will be buffered if it isint main(int argc, char** argv)
{
while (1)
{
sleep(1);
printf("hello!\n");
}
}
redirected to a pipe, like:
a.out | tee tmp.log
After some investigation, I found the behaviour is documented in setbuf(3) man page:
The three types of buffering available are unbuffered, block buffered, and line buffered. When an output stream is unbuffered, information appears on the destination file or terminal as soon as written; when it is block buffered many characters are saved up and written as a block; when it is line buffered characters are saved up until a newline is output or input is read from any stream attached to a terminal device (typically stdin).... Normally all files are block buffered. When the first I/O operation occurs on a file, malloc(3) is called, and a buffer is obtained. If a stream refers to a terminal (as stdout normally does) it is line buffered. The standard error stream stderr is always unbuffered by default....
There are two ways to solve the problem. First, call fflush(stdout) after printf.
Second, call setlinebuf(stdout) at the startup of the program.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
